신림선 무인운전을 위한 K-AGT와 KRTCS간 안전·운영 요구사항 검증 S/W연구
초록
본 논문에서는 신림선에 적용 예정인 차량(K-AGT)과 열차제어장치(KRTCS) 간 안전 및 운영 요구사항을 검증하기 위한 시험에 대해 설명한다. 신림선 도시철도에 납품 전 5,000km 주행시험을 통하여 안전 요구사항 31건(표1), 운영 요구사항 52건(표2)을 검증한다. 안전 및 운영 요구사항 검증을 위해 S/W를 통해서 시스템을 구성한다. 시험 항목의 시험 성공 조건은 자동 시험 항목에 대해서 정해진 시간 내에 해당 데이터를 수신하거나 수동 시험 항목에 대해서 사용자가 시험 결과 선택 화면에서 성공을 선택했을 경우이다. 해당 시험을 통해서 차량 및 신호 시스템에 대한 패키지 통합 기술 확보 및 무인운전 실적 확보로 국내외 도시철도 사업에 대한 가격 및 기술 경쟁력 및 수출 경쟁력을 확보할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
Abstract
In this paper, a test to verify the safety and operation requirements between the vehicle (K-AGT) and the train control system (KRTCS) planned to be applied to the Sillim Line is described. 31 safety requirements(table 1) and 52 operational requirements(table 2) are verified through a 5,000km driving test before delivery to the Sillim Line railway. To verify safety and operation requirements, the system is configured through S/W. The test success condition of the test item is when the corresponding data is received within the specified time for the automatic test item or the user selects success on the test result selection screen for the manual test item. Through this test, it is expected it will be able to secure price, technology and export competitiveness for domestic and overseas railroad business by securing package integration technology and manless driving performance for vehicles and signal systems.
Keywords:
safety requirements, operation requirements, K-AGT, KRTCSⅠ. 서 론
신림선 도시철도는 완전무인운전방식으로 운영 도입됨에 따라 열차운행의 안전성과 효율성을 보장하기 위해 수요처에서 요구하는 K-AGT 차량과 KRTCS 신호 시스템 간 안전 및 운영요구사항 검증을 통해 완벽한 무인경전철 시스템을 구축하고 성공적인 상용화를 실현하여 안전한 도시철도 건설 및 운영에 기여하고자 한다. K-AGT는 한국형 표준 고무차륜 경량전철을 말하며, 1999년 하반기부터 2004년 말까지 약 5년 2개월에 걸쳐 개발한 한국 최초의 고무 차륜식 경량전철이다. KRTCS는 한국형 무선 기반 열차제어시스템이다. 열차제어시스템은 철도의 안전한 운행을 위한 설비로서 열차운행계획을 관리하는 ATS(Automatic Train Supervision), 선행열차와 후속열차 간 안전거리를 보장하는 ATP(Automatic Train Protection) 및 기타장치로 구성되어 있다. 신림선 도시철도 납품 전에 5,000km 주행시험을 통하여 K-AGT 차량과 KRTCS 신호 시스템의 안전 요구사항 31건 및 운영 요구사항 52건에 대하여 검증하고자 한다. 이를 통해 열차제어 시스템의 완전 국산화를 실현하며, 국내외 철도 신호 사업에 대한 가격 경쟁력 및 기술력을 확보할 수 있다. 또한, 차량 및 신호 시스템에 대한 패키지 통합기술 확보 및 무인운전 실적 확보로 국내외 도시철도 사업에 대한 가격 및 기술 경쟁력 및 수출 경쟁력을 확보할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
Ⅱ. 안전 및 운영 요구사항 검증 S/W
2.1 요구사항 검증을 위한 시스템 구성
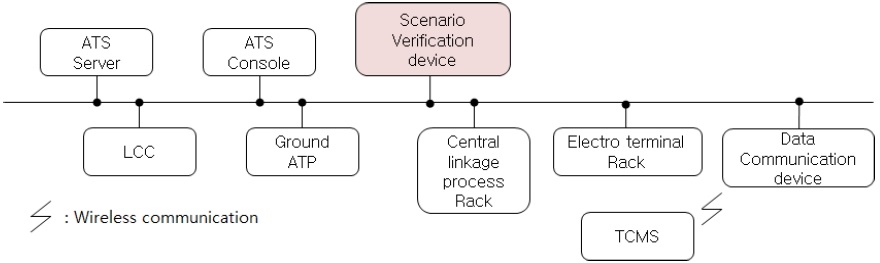
그림 1과 같이 시나리오 검증장치는 ATS 서버와 지상 ATP, 연동장치, TCMS 등과 인터페이스 하여 해당 정보를 파악하여 각 시나리오 시험 시, 각 장치별로 처리가 정상적으로 이루어지는지 확인하여 이를 결과로 저장한다.
자동으로 확인하지 못하는 사항에 대해서는 시험자가 직접 수동으로 입력할 수 있도록 팝업메시지가 나타나 결과를 선택할 수 있도록 한다.
2.2 프로그램 구성
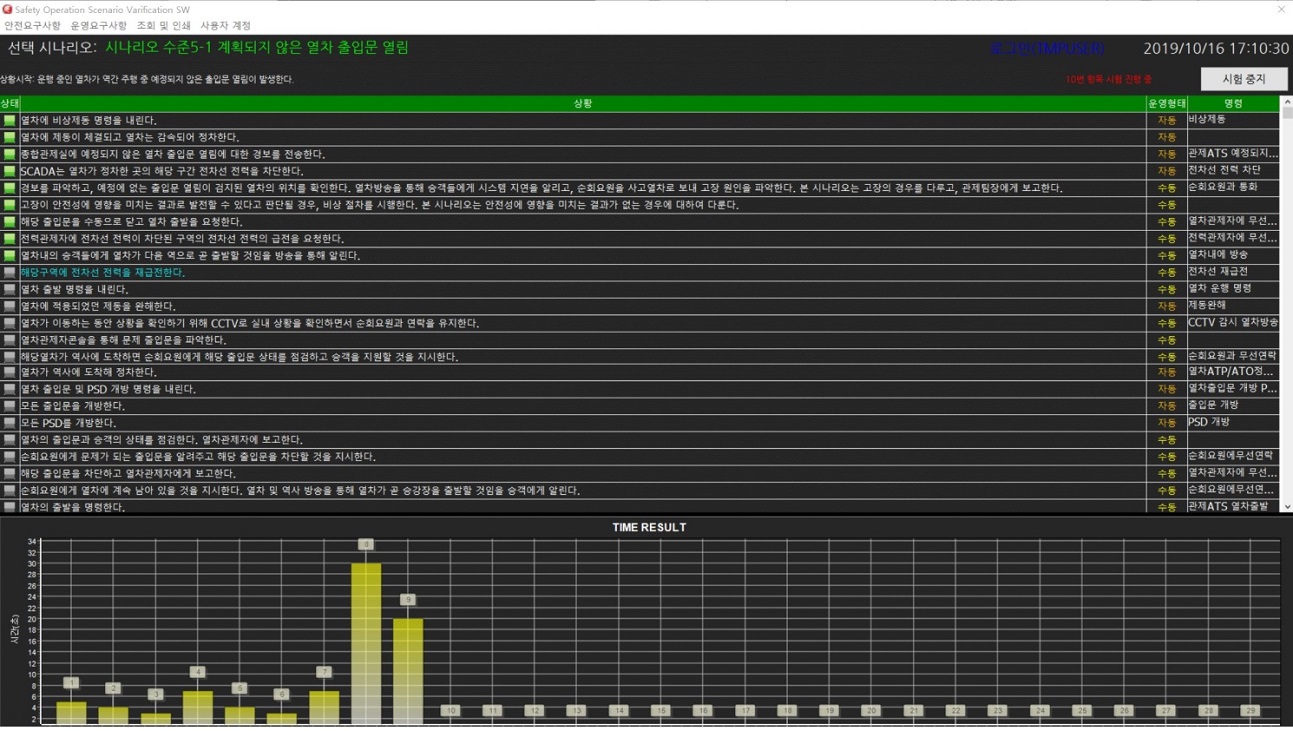
S/W용 프로그램은 COMM, SOSV, WDX로 크게 3가지로 구성된다. COMM은 다른 장치로부터 데이터를 수신 받는 기능을 제공한다. SOSV는 사용자가 선택한 시나리오 검증 절차에 따라서 시나리오의 정상 유무를 체크하는 기능을 제공하며, WDX는 구성 프로그램에 대한 일괄 구동 및 감시 기능을 제공한다. 그림 2는 검증 S/W 화면이며, 그림 3은 프로그램 화면 구성을 설명한 것이다.
검증 하드웨어는 산업용 컴퓨터 1대, 모니터 1대, 키보드 마우스 1SET로 구성되며 연구개발 기간은 2019년 8월부터 2019년 12월까지이다.
Ⅲ. 프로그램 화면
3.1 안전 요구사항 및 운영 요구사항
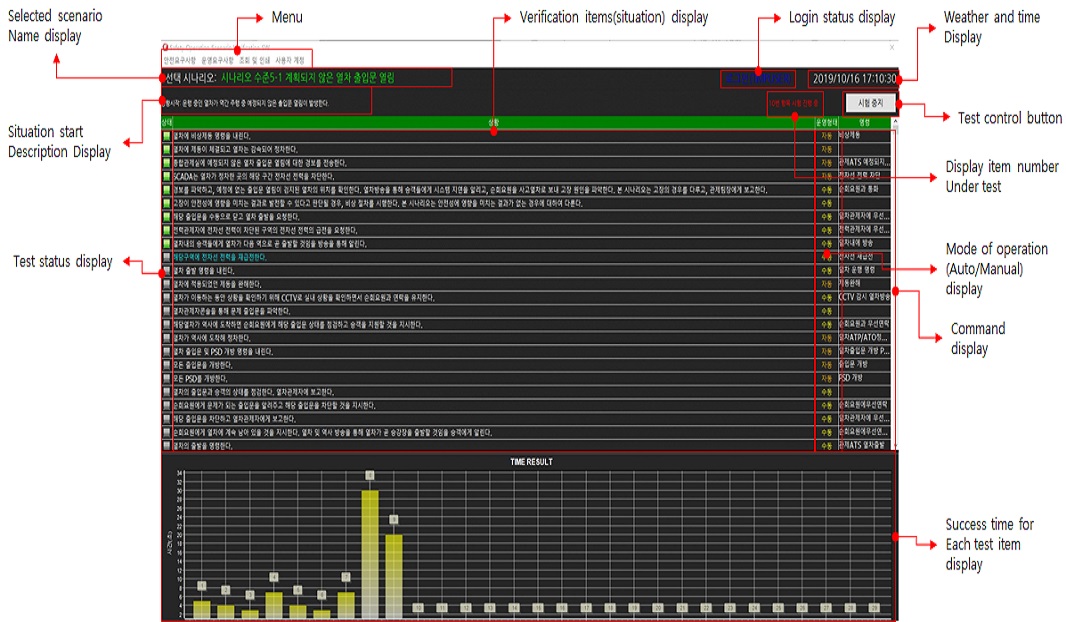
안전 및 운영요구사항 검증 S/W의 세부 기능은 메뉴를 통해 선택 할 수 있다. 각 메뉴는 주 메뉴 명과 보조 메뉴 명 그리고 세부 메뉴 명으로 구성되며, 주 메뉴 클릭 시, 보조 메뉴 명은 풀다운(Pull down) 형식으로 표시되고 보조 메뉴 선택 시, 보조 메뉴 우측에 세부 메뉴가 표시된다.
3.2 조회 및 인쇄
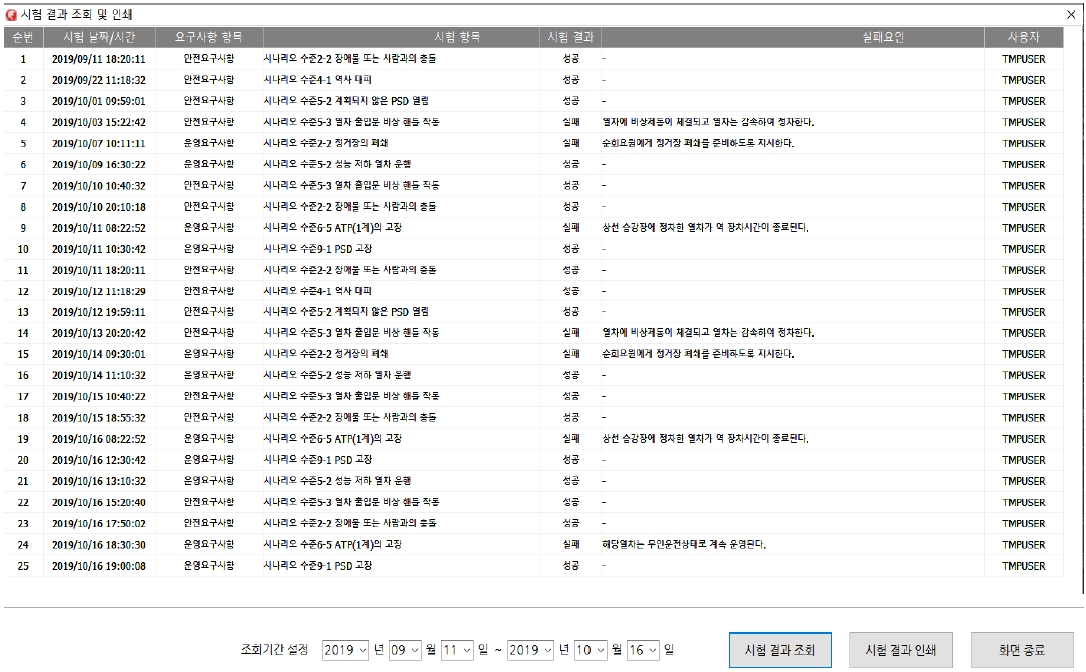
조회 및 인쇄 메뉴는 운영자가 수행했던 시험 내역을 날짜 또는 시나리오 별로 조회할 수 있으며, 조회한 화면을 인쇄할 수 있다. 시험 내역은 순번, 시험 날짜/시간, 요구사항 항목, 시험 항목, 시험 결과, 실패요인 및 사용자를 포함하며, 조회 결과를 그림 4와 같이 화면에 표시한다.
3.3 사용자 계정
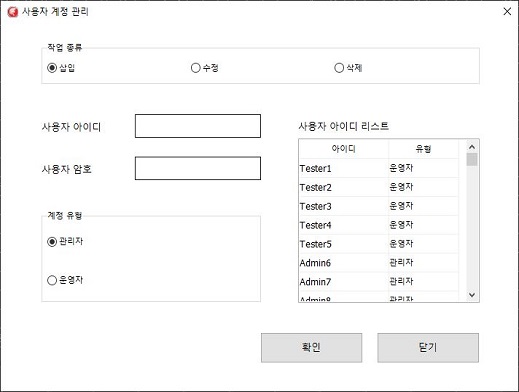
로그인/로그아웃 메뉴를 통해 사용자 계정 정보(아이디/암호) 입력을 통해 로그인을 할 수 있다. 사용자 계정은 최대 20개 추가할 수 있으며, 운영자는 시험만할 수 있고 관리자는 시험 및 계정 관리를 할 수 있다. 사용자 계정 화면은 그림 5와 같다.
3.5 운영형태(자동/수동) 표시
운영자의 개입이 필요여부에 따라 ‘자동’ 혹은 ‘수동’을 표시한다. '수동’으로 입력된 시험 항목은 해당 시험차례에 화면 중앙에 확인 창이 표시되고, ‘성공’ 또는 '실패’ 버튼을 클릭하여 시험에 대한 성공 또는 실패를 결정한다.
3.6 명령 표시
운영자, 열차 혹은 기타 주체가 제어하는 명령을 표시한다. (예시 : 비상제동, 순회요원과 통화, 열차 내에 방송, PSD 개방, 출입문 개방 등)
3.7 시험 항목 별 시험 성공시간 표시
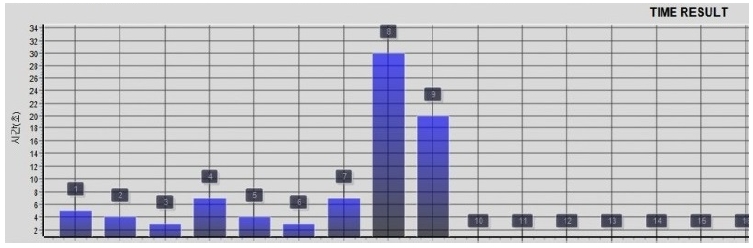
시험 항목 별 성공시간을 막대그래프 형태로 표시하면 그림 6과 같다. 각 막대 상단에 표시되는 숫자는 시험 항목 번호를 의미하며, 막대 높이는 성공시간(단위: 초)을 의미한다.
3.8 WDX
WDX는 등록된 프로세스의 실행 여부 및 각 데이터 송·수신 상태를 주기적으로 표시한다. WDX에 등록된 프로세스는 종료되지 않도록 감시되며, 프로세스가 종료되어도 재실행된다.
이 외에도 WDX은 SMV의 Replay 및 화면 캡처를 위한 버튼이 있어 해당 기능을 수행할 수 있다.
Ⅳ. 시험 진행절차
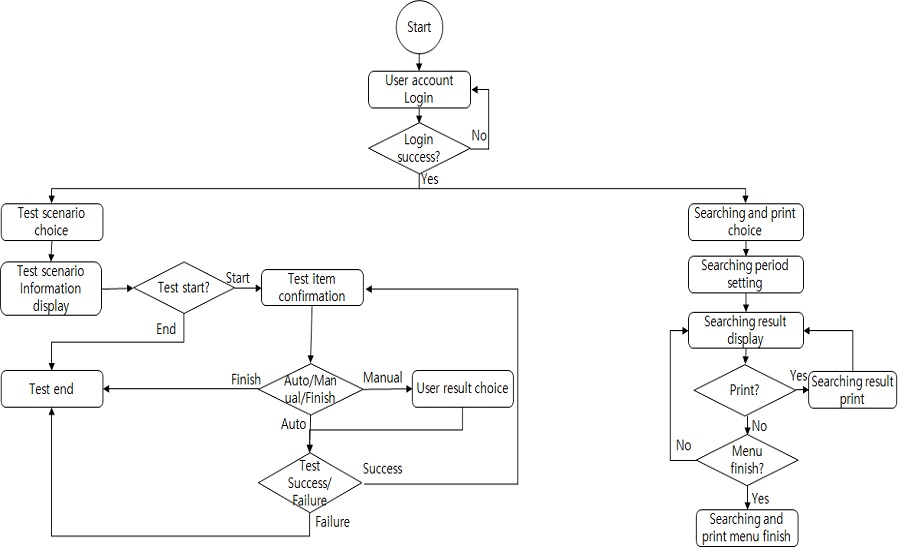
안전 및 운영요구사항 검증 S/W를 통한 시험 진행 절차는 그림 7과 같으며, 안전 및 운영 요구사항 검증 S/W를 통한 시험을 진행하기 위해서는 사용자 계정을 통한 로그인을 마쳐야 한다. 로그인을 하지 않으면 시험 메뉴 선택 및 조회 및 인쇄 선택이 불가능하다.
4.1 시험성공 조건
시험 항목의 시험 성공 조건은 자동 시험 항목에 대해서 정해진 시간 내에 해당 데이터를 수신하거나 수동 시험 항목에 대해서 사용자가 시험 결과 선택 화면에서 성공을 선택했을 경우이다. 보통 자동 시험의 경우 ATP 정보에 대한 항목은 0.5초, ATO 정보에 대한 항목은 3초 이내로 수신된다.
S/W 검증장치는 항목 별 적정시간을 고려하여 30초로 설정 되어 있기 때문에 30초 이내에 ATP 정보 및 ATO 정보가 수신되면 성공으로 판단한다. 만약 자동 시험 항목에 대해서 정해진 시간 내에 해당 데이터를 수신하지 못하거나 수동 시험 항목에 대해서 사용자가 시험 결과 선택 화면에서 실패 선택 시, 시험은 실패하게 된다.
4.2 시험종료 조건
시험 시나리오 종료 조건은 사용자가 시험 종료를 선택하거나 시험 중인 항목의 시험 결과가 실패할 경우이다. 실패조건은 ‘자동’일 경우 정해진 시간 동안 성공 조건에 해당하는 데이터를 미수신할 때 이며, ‘수동’일 경우 사용자가 시험 결과 선택 화면에서 실패를 선택할 때이다.
4.3 시험결과 조회 및 인쇄 조건
사용자가 설정한 기간에 해당하는 시험 결과에 대해서 조회 및 인쇄가 가능하다. 관리자 권한으로 로그인 할 경우에 모든 시험 결과에 대해 조회 및 인쇄가 가능하며, 운영자 권한으로 로그인 할 경우에 해당 운영자가 시험한 결과만 조회 및 인쇄가 가능하다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
본 논문은 국토교통과학기술진흥원의 철도기술연구사업(실용화 문턱과제)인 ‘신림선 무인운전을 위한 K-AGT 차량과 KRTCS 열차제어시스템 상호간 안전운영 요구사항 검증 연구사업'(19RTRP-C148749-02)의 일환으로 수행되었으며, 신림선 도시철도에서 완전무인운전 방식으로 운행됨에 따라 열차운행의 안전성과 효율성을 보장하기 위해서 무인운전에 대한 안전 및 운영요구사항 검증이 반드시 선행되어야 하며, 열차운행계획·선로선형·열차형식·열차운영시나리오 등에 의해 열차제어시스템의 소프트웨어가 맞춤 제작되도록 하고 신뢰성과 안전성이 검증된 제품을 도입되도록 검증되어야 한다.
Acknowledgments
이 논문은 국토교통부 철도기술연구사업의 실용화 문턱과제 연구비지원(19RTRP-C148749-02)에 의해 수행되었음 (This work was supported by the research grant of 19RTRP-C148749-02)
References
- Korea Railroad Research Institute, https://www.krri.re.kr, . [accessed: Jan. 20, 2020]
-
Yong-Sam Kang, "A study on interoperability and applicability of the Korean Radio based Train Control System(KRTCS)", The Transactions of the Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers, Vol. 65, No. 6, pp. 1095-1102, Aug. 2016.
[https://doi.org/10.5370/KIEE.2016.65.6.1095]

-
Chan-ho Kim, Jong-won Park, Kang-gyoo Lee, Dong-il Sung, and Hak-sun Yun, "Development of Standard Specification of Korea Radio based Train Control System(KRTCS-2) for Conventional & High Speed Railway", Journal of the Korean Society for Railway, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 736-743, Dec. 2016.
[https://doi.org/10.7782/JKSR.2016.19.6.736]

-
Shin-hyung Cho, Young-hyun Seo, Seung-young Kho, and Sung-mo Rhee, "Establishing the Methodology of Economic Analysis to Take into Account Opportunistic Valuation for a Radio Communication & Train Control System", Journal of the Korean Society for Railway, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 373-379, Jun. 2016.
[https://doi.org/10.7782/JKSR.2016.19.3.373]

-
Kang-Gyoo Lee, Jong-gwoan Choi, Dong-Il Sung, Hak-Sun Yun, Jong-Won Park, You-Ho Kim, Nam-Hyoung Lee, and Jong-Cheon Yoo, "Expanding Plan Study of KRTCS-2(Korean Radio Train Control System for Conventional & High Speed Railway)", The Transactions of the Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers, Vol. 66, No. 3, pp. 533-539, Aug. 2017.
[https://doi.org/10.5370/KIEE.2017.66.3.533]

- Jong-Ki Kim, Hyu-Hyoung Choi, and Kee-Seo Lee, "A Construction Method for CBTC Communication Networks", Journal of the Korean society for railway, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 257-263, Jun. 2006.
-
Chan-ho Kim, Gong-jun Jeon, Kang-gyoo Lee, Dong-il Sung, Seung-ah Choi, and Hak-sun Yun, "A Study on the Method with Design Criteria of KRTCS using LTE-R Radio Network for Conventional & High Speed Railway Through the Analysis of Design Criteria of the Trackside System", International Journal of Railway, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 34-39, Jun. 2017.
[https://doi.org/10.7782/IJR.2017.10.2.034]

-
Minseok Kim, Minkyu Kim, Doogyum Kim, and Jongwoo Lee, "Analysis of Distance between ATS and ATP Antenna for Normal Operation in Combined On-board Signal System", International Journal of Railway, Vol. 5, No. 2, pp. 77-83, Jun. 2012.
[https://doi.org/10.7782/IJR.2012.5.2.077]


1992년 2월 : 동양공업전문대학 기계설계(전문학사)
2004년 2월 : 충주대학교 기계설계공학(학사)
2006년 2월 : 충주대학원 열유체공학(석사)
1996년 11월 ~ 현재 : 우진산전 차량사업부 연구소장
관심분야 : 철도차량설계

2015년 2월 : 충북대학교 전기공학과 (학사)
2015년 12월 ~ 현재 : 우진산전 차량사업부 주임 연구원
관심분야 : 철도차량설계

2014년 02월 : 호남대학교 정보통신공학과(학사)
2003년 01월 ~ 현재 : 광주도시 철도공사 건설지원팀 부장
관심분야 : 광주 2호선 차량 검수